Fare-free transit is a topic that has been gaining momentum across the country for several years now. The pandemic and heightened public awareness of equity and racial justice issues have brought it even closer to the forefront of our industry, and even on the radar of the general public (as evidenced by the Washington Post feature on the topic). Many large agencies around the country have also already implemented fare programs that provide discounts or free fares for people from low-income households.
Removing fares makes transit service affordable and accessible to all people, including those who are most in need of transportation service, which results in a significant equity-related benefit. We know that low-income and minority populations, as well as a disproportionately large share of essential workers, are most likely to rely on transit, particularly buses (as opposed to rail service, which is often higher-priced). For example, 46 percent of trips on the WMATA Metrobus system are made by low-income residents and 81 percent are made by people of color (those figures for Metrorail are 13 and 45 percent, respectively). In communities where we’ve worked, we’ve heard stories of low-income people walking several miles to access benefits and services because they could not afford the fare to ride the bus. This just reinforces something we already know—that transportation is a fundamental need for everyone.
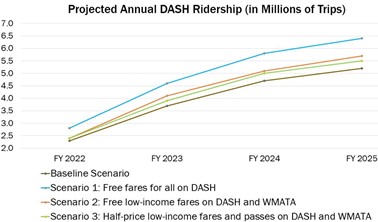
We recently had the privilege of conducting a study for the City of Alexandria, through the MWCOG Transportation-Land Use Connections Grant Program, to evaluate options for implementing a fare program to make transit more accessible to low-income riders. We conducted an in-depth literature and case example review as part of the study which provided lots of valuable information about current fare programs and practices, travel behaviors of low-income individuals, experiences of agencies who have gone fare-free or implemented low-income fare programs, and noteworthy practices related to implementing and marketing fare programs. This review also provided information about the cost and ridership impacts from other “real world” fare program examples. In coordination with City of Alexandria staff, we identified three scenarios of low-income fare programs the City could implement, with free fares on the DASH system (the City’s local transit service) being one of the scenarios (the other two involved free and discounted passes on both DASH and WMATA regional bus services). A description of the methodologies and findings of our study can be found here (see “Low Income Fare Pass Assessment” section).
Conversations around making the DASH system fare-free were already happening before and during our study. Our role was primarily to help decision-makers understand what the impact of their decision would be, particularly with respect to cost and ridership impacts, with the fare-free scenario being compared to other viable options such as providing discounts or free fares for low-income residents only. We were also able to use the findings from our literature and case study review, as well as interviews, to make marketing, administration, and program evaluation recommendations. Our analysis found that free fares on DASH would not only result in the greatest ridership increase but would benefit the most residents (at the lowest per-beneficiary cost), especially compared to more targeted programs that would not benefit many low-income residents who struggle to afford the costs associated with meeting their basic needs but do not qualify for programs such as the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP). Ultimately, the City Council voted as part of its FY 2022 budget to make DASH service free for all riders, at an estimated cost—primarily in terms of foregone fare revenue—of $2.2 million in FY 2022. However, as the pandemic (hopefully) subsides and DASH ridership increases, the financial impact of foregone revenue will increase. In the City of Alexandria, some leaders and residents expressed an opinion that public transit should be seen and treated as a utility that should be free to all users just like others such as libraries, roads, and schools.

Evaluating discounted and fare-free options for this project also involved researching other important considerations such as how to determine eligibility and administer eligibility verification processes (for targeted programs), handling fare payments for discounted fares, addressing the potential for people experiencing homelessness using buses as a form of shelter, and operational impacts such as potential crowding from going fare-free. For many agencies, going fare-free would have implications for ADA complementary paratransit services that would also be an important consideration.
While Foursquare ITP does not have a position as a company on fare-free transit—our purpose is to advise clients on how to meet their own community-specific goals and needs—we are eager to support clients who want to have a meaningful impact on their communities by making transit more affordable while also carefully considering the financial and operational impacts of these decisions.